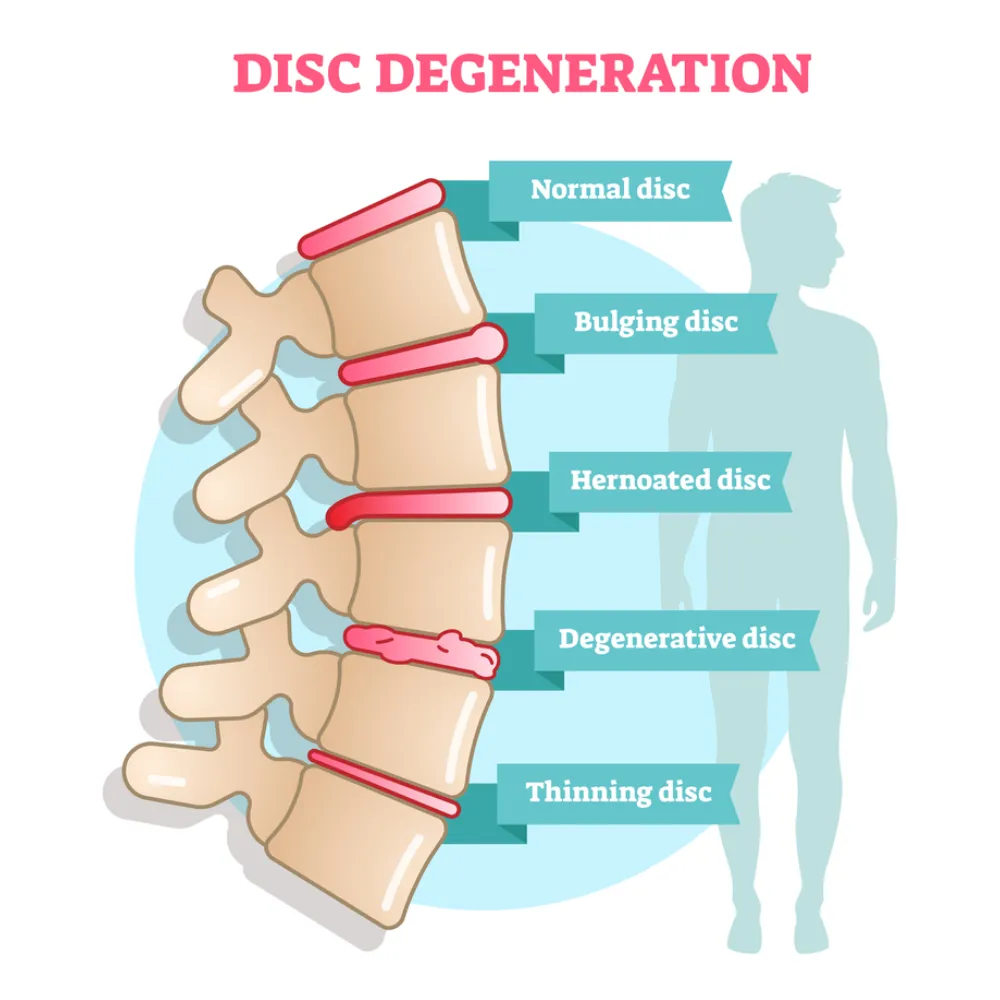
Back pain is a common ailment that can stem from various sources, and one of the most prevalent causes is issues with the spinal discs. Two terms that often get thrown around in discussions about spinal problems are “bulging disc” and “herniated disc.” While these conditions may sound similar, they have distinct differences that can significantly impact treatment options and outcomes. In this blog, we’ll break down the key disparities between a bulging disc and a herniated disc, making it easy for you to understand.
What is the Difference Between a Bulging and a Herniated Disc?
Distinguishing between these two conditions isn’t always straightforward without a proper medical evaluation. If you’re experiencing back pain, particularly if it radiates down your leg or arm, it’s imperative to consult a healthcare professional. They can employ imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans to precisely identify the issue.
What Is A Bulging Disc?
In a bulging disc, the outer layer of the disc (known as the annulus fibrosus) becomes weakened and stretches beyond its usual limits. Importantly, it doesn’t rupture or tear, meaning the inner gel-like substance (nucleus pulposus) remains contained within the disc.
Causes: Bulging discs typically develop due to age-related wear and tear on the disc or repetitive strain. Injury can also play a role in causing them to develop.
Symptoms: Bulging discs can be asymptomatic, but they may cause mild to moderate discomfort or pain in the affected area. Numbness or tingling can also occur, but these symptoms are typically milder when compared to those associated with a herniated disc.
Treatment: Conservative treatments are usually effective in managing bulging discs. These may include physical therapy, pain management techniques, anti-inflammatory medications, and lifestyle modifications. Bulging disc cases rarely require surgical intervention.
What Is A Herniated Disc (aka Slipped Disc)?
A herniated disc involves a more severe issue where the outer layer of the disc ruptures or tears. This tear allows the inner gel-like substance (nucleus pulposus) to leak out of the disc. This escape can press on nearby nerves, causing a variety of symptoms that can be stronger and affect a wider area.
Causes: Herniated discs often result from more significant trauma or injury, such as a sudden, forceful event, lifting heavy objects incorrectly, or a severe accident.
Symptoms: Herniated discs tend to cause more intense pain, which can often radiate down the arms or legs, depending on the location of the affected disc. This can lead to weakness, numbness, or tingling in these areas. The symptoms are typically more pronounced and may require more immediate attention.
Treatment: Treatment for herniated discs can also involve conservative measures like physical therapy, pain medication, and epidural steroid injections. However, in severe cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if there is significant nerve compression, surgery may be recommended to remove or repair the damaged disc.
In Conclusion:
While both conditions involve issues with spinal discs and can cause discomfort, the key difference is in the severity of the damage to the disc’s outer layer and the resulting symptoms. Bulging discs are less severe, with the disc protruding but remaining intact, while herniated discs involve a tear or rupture and often lead to more intense pain and neurological symptoms. If you suspect you may be dealing with either of these spinal conditions, it’s imperative to seek medical advice promptly. This will help determine the most suitable course of action for your spinal health, ensuring you can continue to enjoy life with a spine that’s feeling fine.