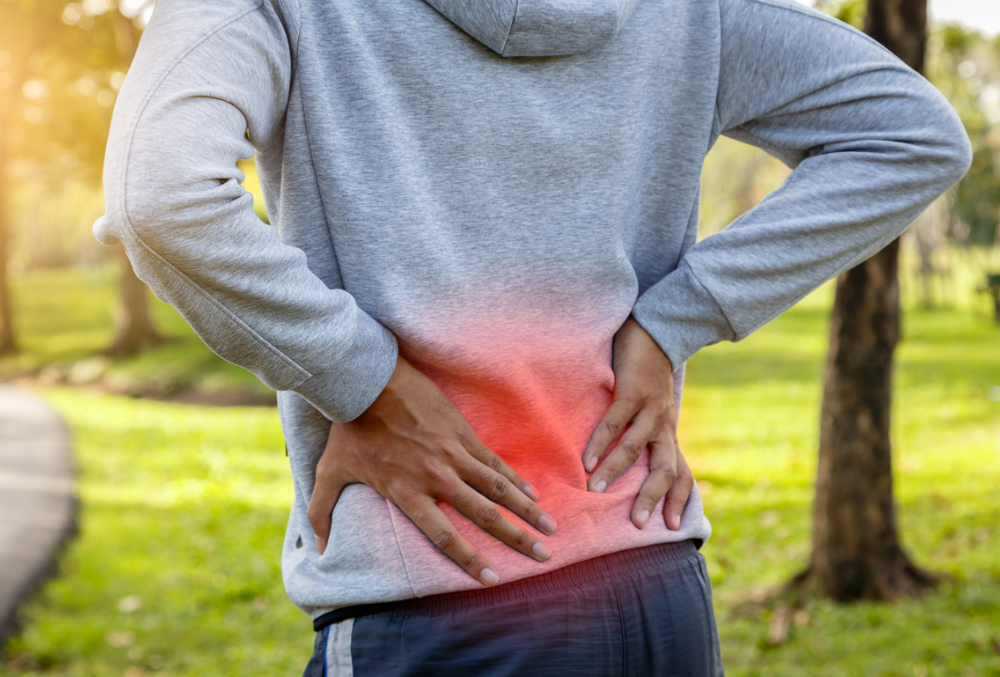
Lower back pain is a common ailment that affects people of all ages and genders, but it’s especially prevalent in women. It can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain, impacting daily activities and quality of life. Understanding the causes of lower back pain in females is crucial for prevention and effective management. In this article, we’ll explore the various factors that contribute to lower back pain in women and discuss strategies for relief.
Muscle Strain and Overuse
One of the most common causes of lower back pain in women is muscle strain and overuse. This can occur due to activities such as heavy lifting, sudden movements, or prolonged sitting or standing. The muscles in the lower back can become strained or irritated, leading to pain and discomfort.
Poor Posture
Poor posture is another culprit behind lower back pain in females. Slouching or sitting with improper alignment can put undue stress on the muscles and structures of the lower back, leading to pain over time. Improving posture through awareness and corrective exercises can help alleviate and prevent this type of pain.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a significant factor that can contribute to lower back pain in women. As the uterus expands during pregnancy, it can shift the woman’s centre of gravity and put additional strain on the lower back. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can also loosen the ligaments and joints in the pelvic area, exacerbating back pain.
Menstrual Cramps
Lower back pain is a common occurrence for many women during menstruation, often referred to as menstrual cramps. These cramps arise from the uterus contracting to expel its lining. Consequently, the discomfort can extend to the lower back, resulting in varying degrees of discomfort, and occasionally, intense pain.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones, is more common in women, especially as they age. This condition can lead to fractures in the vertebrae of the spine, resulting in lower back pain. Proper nutrition, regular exercise, and bone-strengthening medications can help manage osteoporosis and prevent associated back pain.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is characterized by the abnormal growth of uterine lining tissue outside the uterus. This can result in inflammation and scarring, causing symptoms like lower back pain, pelvic discomfort, and painful menstrual periods. Treatment approaches for endometriosis vary and may involve medication, hormonal therapy, or surgical intervention, depending on the condition’s severity.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections are more common in women and can cause lower back pain along with other symptoms such as a burning sensation during urination and frequent urge to urinate. UTIs can lead to inflammation in the bladder and surrounding tissues, causing discomfort in the lower back area.
Stress and Emotional Factors
Stress and emotional factors can also contribute to lower back pain in women. Chronic stress can cause muscle tension and tightness, leading to pain in the lower back. Additionally, emotional factors such as depression and anxiety can exacerbate existing pain and make it more challenging to manage.
Conclusion
Lower back pain is a prevalent issue among women, but understanding its causes can help in finding effective solutions. Whether it’s muscle strain, poor posture, pregnancy-related discomfort, or underlying medical conditions like endometriosis or osteoporosis, there are various ways to address and alleviate lower back pain. By practising good posture, engaging in regular exercise, managing stress, and seeking appropriate medical care when needed, women can take steps to reduce the impact of lower back pain on their daily lives and overall well-being